Review and Analysis of Floating Energy Infrastructure and ...
Part 1: Review of Floating Energy Infrastructure, LNG Consumption, and Gas Power Plants for AI Data Centers
Floating Energy Infrastructure
Floating energy infrastructure, particularly Floating Liquefied Natural Gas (FLNG) and Floating Storage and Regasification Units (FSRUs), represents a transformative approach to energy production and distribution. Unlike traditional onshore LNG facilities, FLNG vessels enable the liquefaction of natural gas directly at sea, allowing access to remote offshore gas reserves without the need for extensive pipeline networks. Similarly, FSRUs provide flexible regasification and storage solutions, enabling rapid deployment in regions lacking fixed infrastructure. This mobility and scalability make floating infrastructure ideal for monetizing stranded gas assets and meeting energy demands in emerging markets.
Key advantages include:
Cost Efficiency: FLNG and FSRUs reduce capital expenditure by eliminating the need for onshore plants and long pipelines.
Speed to Market: Projects can be deployed faster, with conversions of existing LNG carriers often completed in 2-4 years.
Flexibility: Vessels can be relocated to new fields or markets, adapting to changing demand or resource availability.
Environmental Impact: Floating solutions can minimize land disruption and integrate technologies for carbon capture or cleaner fuel production, such as blue and green ammonia.
Source: https://www.alliedmarketresearch.com/floating-liquefied-natural-gas-market-A15554
However, challenges persist, including high initial conversion costs, complex offshore operations, and exposure to volatile LNG prices. Despite these, the global push for cleaner energy and the need to replace coal and oil with natural gas positions floating infrastructure as a critical component of the energy transition.
Graphic: FLNG Market Growth Projection
FLNG Market Size Projection
Source: Allied Market Research, illustrating the projected growth of the FLNG market to $51.6 billion by 2032 at a CAGR of 10.8%.
LNG Consumption
Global LNG consumption has surged, driven by the shift toward cleaner energy sources. In 2024, LNG demand reached approximately 400 million metric tons per annum (mtpa), with projections estimating growth to 700 mtpa by 2040. Asia, particularly China and India, accounts for the largest share of demand, fueled by industrialization and policies phasing out coal. Europe has also increased LNG imports to replace Russian pipeline gas, with floating regasification units playing a pivotal role in rapid terminal deployment.
LNG’s appeal lies in its lower carbon emissions compared to coal (up to 50% less CO2 per unit of energy) and its reliability as a baseload power source. However, supply constraints, geopolitical risks, and competition from renewables pose challenges. Floating LNG infrastructure mitigates some of these by enabling access to diverse gas sources, but market volatility and regulatory shifts remain key considerations.
Gas Power Plants for AI Data Centers
The rapid growth of artificial intelligence (AI) has driven unprecedented energy demand, particularly for data centers powering AI training and inference. These data centers require reliable, high-capacity energy sources to operate 24/7, and gas-fired power plants, supported by LNG, are increasingly critical to meeting this need. Unlike intermittent renewables, gas power plants provide consistent baseload power, making them ideal for supporting the energy-intensive operations of AI data centers. Additionally, natural gas emits significantly less CO2 than coal, aligning with sustainability goals of tech companies.
Floating LNG infrastructure plays a vital role in this ecosystem by supplying gas to coastal power plants located near data centers, particularly in regions like Asia and North America. For example, FSRUs can deliver LNG to regasification terminals, which then feed gas to power plants, ensuring a stable energy supply. As AI adoption accelerates, the demand for gas power plants is expected to grow, driving investment in LNG infrastructure and reinforcing the strategic importance of floating solutions.
Source: https://www.goldmansachs.com/insights/articles/AI-poised-to-drive-160-increase-in-power-demand
Part 2: Analysis of Golar LNG Company
Company Overview
Golar LNG Limited (NASDAQ: GLNG), headquartered in Hamilton, Bermuda, is a leading operator in the LNG midstream sector, specializing in floating energy infrastructure. Founded in 1946, Golar has evolved from a traditional LNG shipping company into a pioneer of FLNG and FSRU solutions. The company operates through three segments: FLNG, Shipping, and Corporate and Other, with FLNG being the primary revenue driver.
Golar’s fleet includes two operational FLNG vessels, notably the Hilli Episeyo, the world’s first converted FLNG, and the Gimi, which began operations in 2025 on the Greater Tortue Ahmeyim project offshore Mauritania and Senegal. The company recently exited the LNG shipping segment by selling the Golar Arctic in February 2025, focusing entirely on FLNG growth.
Strategic Strengths
Leadership in FLNG: Golar’s Hilli Episeyo has a proven track record, achieving 100% commercial uptime and offloading 128 cargoes by Q4 2024. The Gimi further strengthens Golar’s portfolio, with a 20-year contract boosting its EBITDA backlog to $11 billion.
Innovative Partnerships: Golar collaborates with industry leaders to explore blue and green ammonia production and carbon reduction in LNG, aligning with global-decarbonization goals.
Financial Discipline: In Q4 2024, Golar reported $68 million in Distributable Adjusted EBITDA (excluding overproduction) and acquired full ownership of Hilli for $90 million, enhancing cash flow potential.
Growth Pipeline: Golar secured a Final Investment Decision (FID) for a 3.5 mtpa MK II FLNG unit for delivery by 2027, with long-term charters likely involving Shell as an offtaker.
Graphic: Golar LNG FLNG Utilization
Hilli Episeyo Cargo Offloads
Source: Golar LNG Q4 2024 Presentation, highlighting Hilli Episeyo’s 128 cargo offloads and 100% uptime, though currently at 55% capacity until 2027 redeployment.
Challenges and Risks
Market Volatility: Golar’s Q4 2024 revenue of $66 million missed estimates of $67.42 million, reflecting exposure to LNG price fluctuations.
Underutilization: The Hilli is currently at 55% capacity until its redeployment in Argentina in 2027, limiting near-term cash flows.
Geopolitical Risks: Operations in regions like West Africa expose Golar to regulatory and political uncertainties.
Competition: Peers like Cheniere Energy and Excelerate Energy challenge Golar’s market share, though Golar’s FLNG focus provides a niche advantage.
Financial Performance
As of April 2025, Golar’s stock price is approximately $39.51, with a 52-week range of $36.72–$44.36. The company pays a quarterly dividend of $0.25 per share, yielding 2.57%. Analyst consensus rates GLNG as a “Strong Buy,” with an average 12-month price target of $48.70, implying a 23% upside from current levels. Recent upgrades include DNB Markets’ $48 target and Stifel’s $55 target, reflecting optimism about FLNG growth.
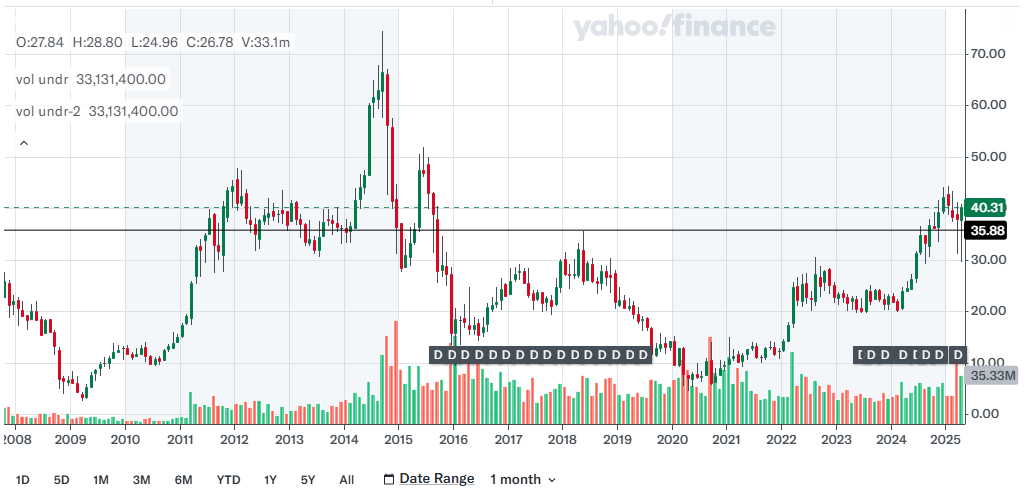
Graphic: Golar LNG Stock Performance
GLNG Stock Chart
Source: Yahoo Finance, showing GLNG’s 52-week stock price range and technical support near $36.
https://finance.yahoo.com/quote/GLNG/chart
Industry Positioning
Golar’s focus on FLNG positions it to capitalize on growing LNG demand, particularly in Asia and Africa. Its exit from volatile LNG shipping reduces exposure to declining spot rates, while long-term FLNG contracts provide revenue stability. The company’s exploration of ammonia and carbon reduction aligns with ESG trends, potentially attracting sustainability-focused investors.
Part 3: Investment Thesis
Thesis Overview
Golar LNG presents a compelling investment opportunity due to its leadership in the high-growth FLNG sector, strong contract backlog, and alignment with global energy trends. The proposed investment strategy is to buy GLNG at $36, targeting a price of $67, with a stop loss at $30.
Rationale
Entry at $36: The stock is near its 52-week low of $36.72, offering a favorable entry point with limited downside. Technical indicators suggest support at this level, with potential for a breakout above $40.
Target Price of $67: A $67 target aligns with Golar’s historical price-to-earnings ratio of 20x and analyst projections of earnings growth driven by Gimi operations and the MK II FLNG FID. This represents an 86% upside, achievable within 18–24 months if LNG demand and FLNG utilization rise as projected.
Stop Loss at $30: A stop loss at $30 limits downside risk to 16.7%, protecting against unexpected market downturns or operational setbacks. This level is below key support at $32, ensuring the position is exited if the thesis weakens.
Risk-Reward Profile: The trade offers a risk-reward ratio of 1:5 (risking $6 for a potential $31 gain), making it attractive for growth-oriented investors.
Supporting Factors
Analyst Optimism: Analyst price targets range from $42 to $56, with historical data showing 85.71% of trades profitable over two years when following top analysts.
Macro Tailwinds: Rising LNG demand, energy needs for AI data centers, and Europe’s shift to LNG imports support Golar’s growth outlook.
Company Execution: Golar’s 400% share price increase since 2019 and strategic focus on FLNG demonstrate strong management execution.
Risks to Monitor
LNG price volatility or delays in FLNG deployment could impact earnings.
Geopolitical disruptions in key operating regions.
Increased competition or technological shifts in the energy sector.
Conclusion
Golar LNG is well-positioned to benefit from the global energy transition through its innovative FLNG solutions and strategic focus on high-margin projects. The proposed investment at $36 with a $67 target and $30 stop loss offers a high-reward opportunity with manageable risk, supported by strong fundamentals and market trends. Investors should monitor quarterly earnings and FLNG project updates to ensure the thesis remains intact.
Graphic Links and Descriptions
Below are the direct links to the graphics referenced in the report, along with brief descriptions to provide context in case the links are not rendering:
FLNG Market Growth Projection
Link: FLNG Market Size Projection
Description: A chart from Allied Market Research showing the FLNG market size growing from $19.2 billion in 2022 to a projected $51.6 billion by 2032, with a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 10.8%. The graph highlights the increasing adoption of FLNG solutions globally.
Growing Energy Demand for Data Centers
Link: Data Center Gas Demand Projection
Description: A bar chart from S&P Global Ratings illustrating the projected natural gas demand for U.S. data centers, rising to 3-6 billion cubic feet per day (bcf/d) by 2030, driven by AI and cloud computing growth.
Golar LNG FLNG Utilization
Link: Hilli Episeyo Cargo Offloads
Description: A slide from Golar LNG’s Q4 2024 investor presentation, detailing the Hilli Episeyo’s performance, including 128 cargo offloads since inception and 100% commercial uptime. It notes the current 55% capacity utilization until redeployment in 2027.
Golar LNG Stock Performance
Link: GLNG Stock Chart
Description: A 1-year stock price chart for GLNG from Yahoo Finance, showing the 52-week range of $36.72–$44.36 with technical support near $36. Select the 1-year view to see the relevant data. Note: You may need to adjust the chart settings to view the exact range.
Disclaimer
This analysis is provided for educational purposes only and does not constitute investment advice. Investing in securities involves risks, including the potential loss of principal. Past performance is not indicative of future results. Investors should conduct their own research and consult with a qualified financial advisor before making any investment decisions. The author is not responsible for any financial losses incurred as a result of using this information.